Covid-19 vaccine
How close we are to a Covid-19 vaccine research teams in the
UK have released promising results from early trials but once a vaccine is
Developed how do we
make sure that everyone gets it this is inside story the race for a Covid in
nineteen vaccine is gathering pace
Scientists around the world are competing to develop a safe
and effective treatment that may help end the pandemic years of research
has been completed in just a few months a team at Oxford
University in the UK has released promising results from early trials but
whilst
There’s excitement doctors warn there's still a long way to
go before a vaccine is widely available we'll bring in our guests in just a
moment but
first this report from paul brannan phase 1 really couldn't
have gone much better for the oxford team early positive signs now confirmed in
the published research so this is an important milestone on
the path but we we're now moving rapidly forwards to try to evaluate whether
the vaccine actually protects the population by conducting large-scale
trials may have 10,000 people already vaccinated around the world we still need
to see how the vaccine performs in older people who are more at risk of severe
disease than the people we vaccinated in this
study so that's the subject of future work and there'll be
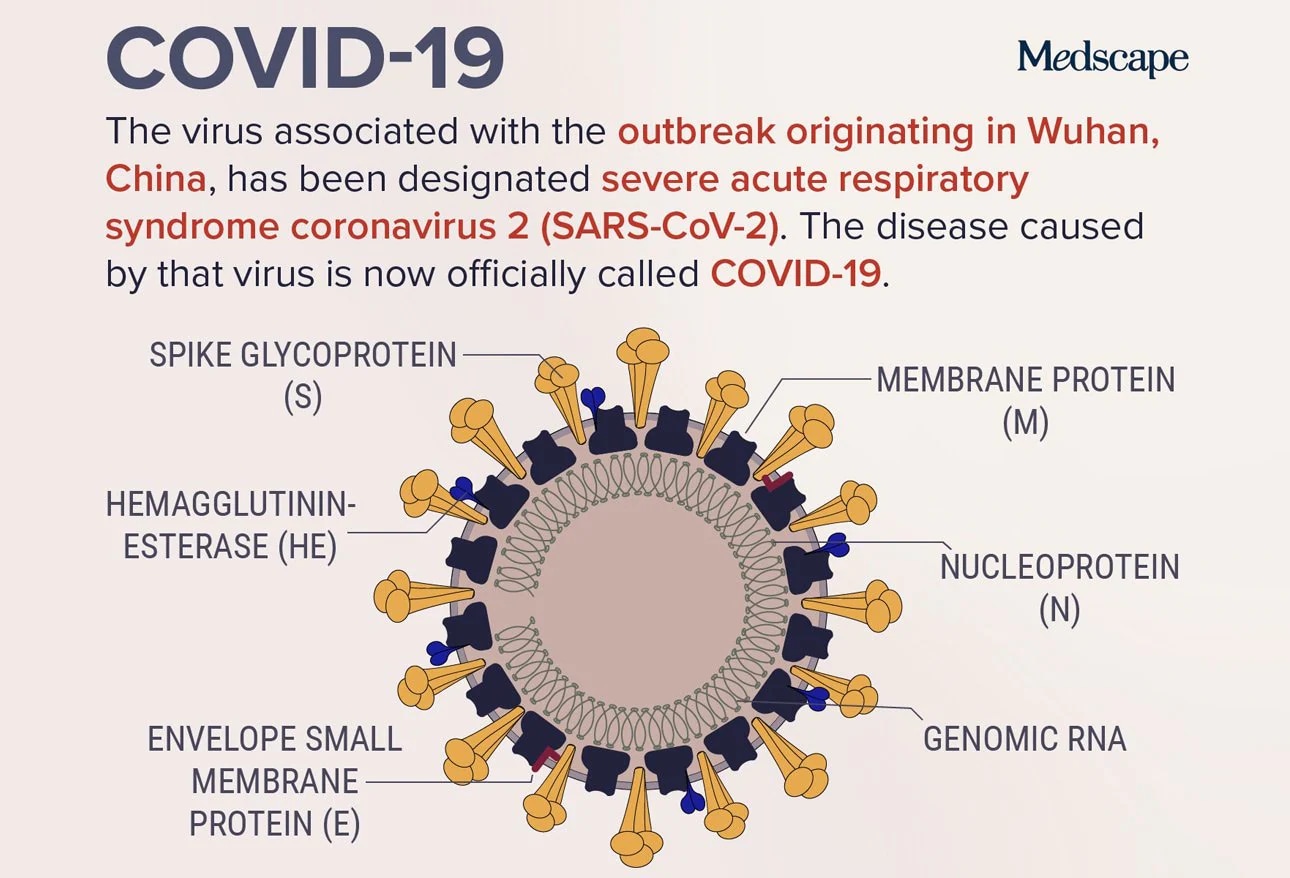
more publications to come the oxford vaccine is adapted from a common
Cold virus found in chimpanzees spike glycoprotein a genetic
material from the Covid 19 virus was added the hope is the human body.
How covid-19 affect in our body
Develop immunity to the spike protein stopping the virus from
entering cells and preventing infection tests indicate the vaccine produces two
Reactions by producing a defensive antibody response as well
as t-cells which attack the infected cells t-cell response peaked just 14 days
after
Volunteers were injected antibody response peaked at 28 days
and side effects were minor mainly just tiredness and headaches treated with
paracetamol I'm hopeful I got my fingers crossed but to say
that I'm in 100% confident that we'll get a vaccine this year or indeed next
year is
alas just you know an exaggeration we're not there yet this
is a hugely encouraging result for the team here in Oxford but provoking an
Immune reaction is just the first stage in vaccine
development phase 3 trials or already underway in the UK South Africa and
Brazil are looking
At issues such as optimal dosage and exactly how much
protection vaccinated people have when exposed to the actual coronavirus nine
in
Ten vaccine projects end in failure and there is no guarantee
that the early promise of the Oxford trials will lead to an effective Covid 19.

Positive step from Oxford University
It is a very positive step Paul Brennan al-jazeera Oxford the
World Health Organization is tracking around 160 possible vaccines against
Covid 19 most are still in the preclinical stage being tested
on animals at least 24 are in phase one where the potential vaccines are given
to a
Handful of people or Phase two where they're tested on
hundreds of people three products have reached phase three trials this involves
Vaccinating thousands of people to check for safety and side
effects these are from the Chinese companies Tsai Novak it's conducting tests
Now in Brazil there's also the University of Melbourne and
Murdoch Children's Research Institute in Australia and the University of Oxford
and AstraZeneca trials in the UK which we mentioned earlier
with the World Health Organization says whichever vaccine does succeed it must
be available to everyone we want a groundswell of political
leaders believing in making a vaccine or therapeutics global public good and
this should not be considered as a charity to those who
cannot afford the advantage of using fairness or access to also poor countries
the
World can really be lifted up and lift itself out of this
pandemic together which can speed up the economic recovery let's bring now
and in Lancaster in the UK Mohammad Minea lecturer in
virology at the University of Lancaster in johannesburg helen ruiz member of
the w-h-
o
strategic advisory group of experts on the Covid 19 vaccine and in hong kong
john nichols clinical professor in pathology at the university
of hong kong a very warm welcome to all of you Helen you are
leading this vaccine trial in South Africa how significant is the response that
Humans have had to the Oxford vaccine well in fact I'm not
leading it but I'm very involved in the vaccine approvals and the science of
vaccine the research going on in South Africa but in terms of
your question it's been very interesting to see that there's been a very
positive response from communities to enrolling in the
vaccine trial for the Oxford vaccine there are three sites recruiting and
wanting to enroll
2,000 people including 50 people living with HIV infection
and people are really queuing up to join the study yeah that's quite
interesting in itself I was wondering how you do get people involved in a
trial.

How the world is going from corona
virus
South Africa is perhaps a little bit unique in the sense that
we've been grappling with those HIV and TB s major epidemics for many years so
we've set up really very experienced clinical trial sites
that are very used to doing both vaccine trials and Prevention trials in
communities
with thousands of participants and the clinical trial sites
also have Community Advisory boards so one of the ways that we do this is that
we talk very strongly to the community about what we want to
do and why we want to do it and they give us equally strong feedback about
acceptability or otherwise and how we should do things so
part of it is community awareness but we've had a lot of media attention as you
can imagine to this because it was the first country to do
urban vaccine trials in the African region so that in itself has created
enormous
Interest okay John so we've got a development here where we
see the development equation of antibodies and T cells excited to you about
this milestone yeah I think that's a very interesting aspect
because we're looking at both the seller community as was the humoral so
We’ve also been using some filing some antibodies but with a
digit Hong Kong is very small so we don't have a clinical trial on vaccines but
so
‘We’ve just been focusing more on these small animals
especially the hamsters and so we think getting both the t-cells as well as the
Humoral immunity is a crucial part okay and Mohammed other
there are a hundred and sixty vaccines in various stages of development
Including I believe one by Lancaster University what stage
you at absolutely I mean there are multiple vaccines and multiple technologies
that are being deployed in different part of the world and
here at the Lancaster University our approach is slightly different what we are
Doing is to take an avian virus the virus that can cause
infection in birds and it's pretty harmless in humans we are using basically
the same
Approach as Oxford but a different backbone that is called
Newcastle disease virus at the moment we have demonstrated its preclinical
Studies and we are doing some animal work including hamster
and mice to demonstrate that it induces the immune responses and as it's
ten so far is pretty encouraging okay Helen as mama says it's
all very encouraging at the moment but we must remember these are very
early days and at what stage is a vaccine ready to be
mass-produced well I guess there's two answers to that one of the things that
we've
done globally as people have invested in these very early
vaccine candidates is to in parallel actually say we can't wait till the end to
Actually identify where we're going to manufacture them so
there's already work going on to identify manufacturing sites existing vaccine
Manufacturers asking and looking at their capacity to change
so that's already being looked at and happened although we don't have yet in
effect maxine but in terms of the vaccine development side of
things all of these findings are extremely encouraging and we have three
vaccines where we've got encouraging findings in terms of the
immune response what we need to find out from much larger Charles than
many thousands of participants is whether those immune
responses are going to turn into either protecting completely from infection or
to
Reduce the severity of disease and those are the the advanced
stage clinical trials which in terms of the Oxford the vaccine they're moving
very quickly but many of these vaccines will move in the next
few months quite quickly into those advanced or called phase 3 clinical
trials and once we have those results and that's when we
really would say and if they're favorable that's what we would say we think
that
we've got a vaccine that is is that we can roll out but we
would also have to then look and say who do we roll it out to because some
Vaccines for example don't work in older people some vaccines
won't many most of these vaccines won't have been tested for example in
Pregnant women so they'll then be a secondary look to say how
many vaccines we have that appear to work limited numbers who would
We prioritize and what the clinical trials is telling us
about how this works absolutely I mean distribution is a very big part of this
discussion
I do want to come on to that in just a moment in terms of the
timeline of course what everybody wants to know is when a vaccine a viable
vaccine is going to be produced and these usually tends to
take a decade don't they the fastest was mumps which took four years is it at
all feasible that a vaccine against covid 19 john could be
produced within a year to 18 months well I handed it out it can be done but
there's so many crucial questions which she's pointed out which we need to look
at basically will it be one dose or two doses birds as in
need an adjuvant in hongkong we have the big problem where 18
to 20 percent of our populations over the age of 55 which is a an age in which
Immune senescence can creep in which means that we may they
may not mount a proper antibody response when we give them.

Situation of Virus now
Vaccine and that's a population which is nice one in our
locality to getting the severe disease so I think it's going to be a big
problem
about as well as point that both the you know who you give it
to and how many doses you give and also realizing that we will be coming up
in another few months to the winter season where we're going
to be also coupling with influenza because right now in many influenza
studies have been put on the back burner and because of COVID
and so I'm worried that we'll get a get we're going to get a double whammy
and in this winter with both influenza as well as resurgence
of COVID and some research which we've been doing is actually looking at the
the how much influenza can actually influence coded
replication because so that's actually one of our greatest fears about what's
going
to happen this coming winter mmm that's only one will be
watching out for every Helen you say got a successful trial of people you've
got a lot
of volunteers but how do you test a vaccine on vulnerable
people how do you test a vaccine on elderly people or people with comorbidities
Well you're obviously going to be I mean I mentioned that
we've got a small subgroup for HIV infected and one of the things there's
several
Things we want to check there one is is the vaccine going to
be safe because the immune system is compromised even if people are on
antiretroviral and the second one is it going to work because
again you've got an immune system that isn't necessarily as robust as
somebody who's not living with HIV so they're you often have
much more rigorous safety mode even more rigorous than we're seeing in the
in the few like the general population so you look carefully
at safety and you look very closely and carefully at the immune response and
that would be the same for older people you'll be
particularly as John was saying interested to say do they amount do they mount
the same
Immune response as we're seeing in younger populations is
that and if they don't is that an indication that this vaccine doesn't work if
it's not
quite as good do we know that we won't know that that's the
problem the immune response if it's there we can't tell you for sure whether it
will we'll protect and if it protects in younger people and
we see a lesser immune response than older people we still can't say for sure
whether that means that we need to give more doses booster
doses or whether we shouldn't be giving it at all because it won't be effective
we're still going to
need clinical data and Mohamed there's a very strong group isn't there that's
calling for what they call challenge trials this is where vaccinated people are
deliberately infected with covid 19
this raises up all sorts of ethical questions doesn't it
because when they've happened in the past they've always had an effective
treatment
but of course there isn't even an effective treatment now for
coronavirus what's your idea of response to challenge trials yes I mean this
idea has been client just to expedite the whole process of trial
Basically what we do any vaccine that come into the human has
to pass through a sort of animal safety trial anyways but this idea is being
Applied before for the flu vaccine validation as you said
that if there are proper treatments available and we understood the disease
enough
that in case any severe consequences appear we would be able
to tackle that but beside that there is a very less motivation really to get
into this trial and by all mean it should be avoided that is my personal
Stance on that but of course there are countries where the
disease is getting down and they are a bit really getting into human trials so
that
they can demonstrate the efficacy in a timely manner but I
think there are other elements that we are talking about for example South
Africa
Countries are moving into the into the population where the
disease is really high so there are alternatives so we can avail doe that up
going
into the human trial is there any evidence Muhammad that in
the rush to find a vaccine that there's there any evidence that safety trials
have
been bypassed or sped up well the element that I am more
worried about is because we are compressing at 10 15 years’ time into 1 year or
so and there is a unprecedented pressure onto scientific
community for the Pharmaceuticals and also for the for the general public to
apply on
but one thing is pretty clear that wuh-oh and other
regulatory authorities they have its hundreds of years of experiences all
together
to really set up pipeline how the vaccine need to be assessed
before it can roll out into the into the manufacturing and the scaling up so
I'm
pretty confident that whatever the outcome of this vaccine
would be that is depending on the nature of the vaccine but when it comes to
the
rules it would only be possible when we have really safety
immunogenicity and all of the parameters that are required for the vaccines to
be rolled out that is the only one will be approved okay
John do you share that confidence I'm a little bit more
skeptical because one of my concerns is that certainly what we've been seeing
in the Hong Kong population is that a lot of when you get the mild disease
and the aged symptomatic is and that's going to be is that
the you know the media says that only about 50% of the population as the adult
Population would actually have the vaccine because I think
that many people say it's and they're very mild disease why should I go vaccine
so
I think there's going to be the incentive for those who just
see this as being a very low disease I should get the vaccine and then the second
is
some of the work which we've been looking at is that it may
prevent a severe disease but will it actually stop replication and the upper
respiratory tract and millet would actually stop transmission
so we may be successful at avoiding a pneumonia but I'm not too sure whether
not
Vaccine themselves may actually will how much they'll stop
transmission and as has been pointed out we're really compressing a
Watson normally a ten year program into one to two years and
there's always this safety aspect I think we've got memories of what happened
With the with the Dinny vaccine in the Philippines we and we
had the side effects and so it meant that people then stopped having their
Measles vaccination so we saw a big outbreak of the measles
so it's always that big concern of the possible side effects leading to the air
the general public staying away from it mmm hello it's such
an interesting point isn't it what if there is a low uptake I mean a recent
poll also showed that 50% of Americans don't want to take a
vaccine they simply don't trust in the process they think it's too sped up it's
too
Politically motivated they've we've got a vaccine but no
one's taking it you may as well not have a vaccine so it's funny that you say
that
because it almost feels like there's a global world divide
debate going on the one hand it is that will there be uptake and so there
would be considerations for example in the country like the
US where it appears that many people might be a reluctant or hesitant and
you've
got an older population in whom it might be much less
effective so you might not be able to immunize a quite a significant proportion
now if
you only have a partially effective vaccine that's the other
thing we haven't mentioned we're not anticipating that every vaccine and
Development a is going to work for B is going to be 100%
effective so what if you only have a partially effective vaccine with partial
uptake
what does that do to community transmission as John mentioned
I mean do it are we able to interrupt transmission what does that do that
you know in the next winter season when you've got many
vulnerable people who are not going to have antibodies and will not have been
Immunized you're going to see resurgence as and resurgence
but I think the other side of that is that if I think about the African region
at the moment is that we are deeply concerned that actually
what we might see is a sort of mass purchasing is called vaccine
nationalization
so that mass purchase
ting and a very restrictive allowance from countries that are manufacturing the
vaccine will that developed the
Vaccine and we saw this with the US with Ramez aveer which is
a therapeutic agent and there will be enormous pressure on
Governments who have done the research and manufacturing of
vaccines there's going to be enormous pressure on them to say well it
has to be my population first so from the African region
we're arguing very strongly that there needs to be equitable access WHO is also
Arguing this incredibly strongly many of the global agencies
we need equitable access because at the end of 2021 what we anticipate is that
we think we might have an effective vaccine but we're not going
to have enough for the whole world so we're saying how do you divide up
limited-access and who should be the priority for that and in fact the
Africa the African Union it has become quite vocal in saying
there needs to be consideration of this now so on the one hand we've got people
Saying we don't want to take the vaccine in the global North
and on the other hand in the global South we're saying we want the vaccine.
Vaccine demands in whole world
And we demand that we
get our fair share so this is these are really
Important we've got to be talking absolutely and distribution
is a key
Part of this argument isn't it Mohamed we've got the UK buying a hundred and ninety million doses of different vaccine it's hedging its
bets it's certainly part of the global north us trying to buy
up as many samples or doses as it can yeah absolutely I think a primary reason
for
Those to buy different vaccine from different manufacturer
are really because none of the vaccine is yet at the stage where everyone can
Count on and the vaccines that you could go might have
contracted those are based on different technologies so just to ensure that
Whatever the technology out of that would become available in
terms of approval and regulatory processes they would be in the position to
Purchase them and to deploy in the field but beside that of
course different vaccines are at different stages so none of that vaccine is
Really at the stage where we can really count on could there
be a global vaccination program well that would be an ideal choice to move to
Move forward because many of the points that we've been
touching upon is really to take up and also the distribution and access I mean
even the vaccines those have been there for centuries really
are not really possible to get them to every point of the need so therefore if
such initiative is is in place at this moment and we are in the position to set
up old international law I think that would be ideal moving forward
as it stands now I can't see anything happening although Gave
here in the in the UK last month I applied to a quite significant amount of
Money to really dedicate on to the Covid 19 vaccine into the
countries where they cannot afford but that is thing that probably need to be
seen when it comes to execution Tom we've gone from the very
top of this show being rather excited about this breakthrough at Oxford
University to the discussion rather downplaying the
significant of these developments throwing up all sorts of questions do you
think a vaccine
is going to be the thing that stops coronavirus pandemic no I
die because I think all the issues which we raised is that it I think if it is
Effective it will there's been mentioned before will probably
decrease the amount of severe pneumonia in the younger to middle age group
but I think that probably is that it will have to be together
with what we've been using now for the past six month which are the social
factors you know the distancing the masks and the contact
tracing together with the dedicated hospitals units to look after the coded
Patients I'm my personal views I think the countries were
saying we wait towards the vaccine we wait till vaccine is are going to be a
bit
Disappointed because it has have we pointed out if the
vaccine is not totally effective if it's not it's got some maybe a few side
effects you
Know what we've found in Hong Kong we've had you know the
lockdown and we've come out early to say now what you know we
can't keep on with this so much restricted isolation so I
think that we all have to try and find a medium we're balancing out yeah use of
a
Vaccine versus antivirals versus preventive measures probably
what we've been also doing for influenza and for other viral diseases for the
Past 80 90 years it's been such an interesting discussion I
do wish we had more time to continue it but we will return.

Conclusion
We are accepting corona virus vaccines in 2021 but if the situation
will not be in control then vaccines will be short and patients will die more
we have to wear masks use sanitizers and make our self-germs free to be careful.
So stay safe. Stay home. Be healthy J

No comments:
Post a Comment